You need a solid technical foundation to ensure search engines can find, read, and rank your content.
This is where an SEO audit comes in. It’s the diagnostic tool that tells you exactly what’s working, what’s broken, and where you’re losing potential visitors.
In this guide, we’ll break down the four critical pillars of an SEO audit and show you how to fix the issues that matter most.
What is an SEO Audit?
An SEO audit is a comprehensive health check for your website.
It analyzes your site’s ability to rank in search engine results pages (SERPs) by looking at technical infrastructure, on-page elements, and off-page authority.
Think of it as a report card.
A good SEO audit tool, like SEOptimer, scans over 100 data points across your entire website in just seconds.
It doesn’t just look at the code; it evaluates how users and search engines experience your site in real time.
The result is a prioritized list of issues giving you a clear roadmap to better rankings.
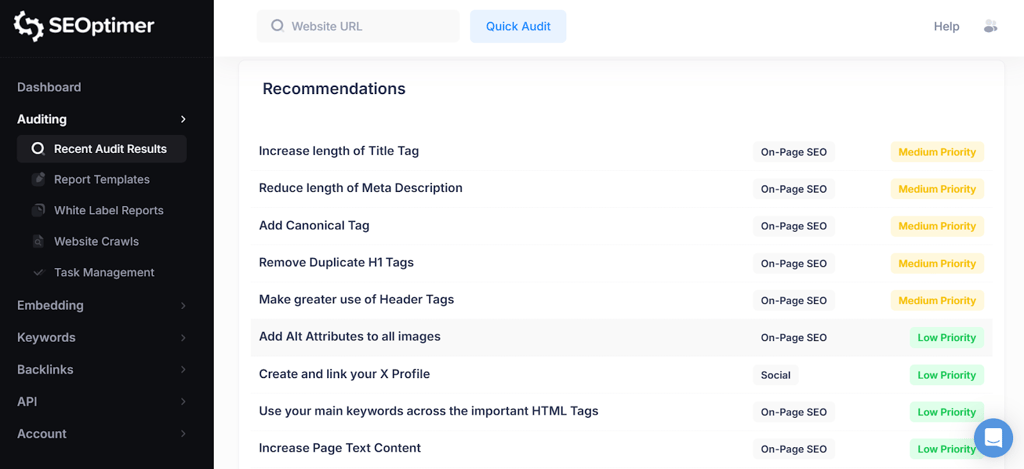
Why Audit Your Site?
Websites are living, breathing entities. You add new pages, update plugins, and change content regularly.
Over time, these changes can accidentally break links, slow down load times, or create duplicate content.
Regular auditing is essential because:
- Algorithms change: Search engines update their ranking criteria thousands of times a year.
- Competitors move fast: Your competitors are likely optimizing their sites right now. An audit helps you stay ahead.
- Errors are invisible: You might not notice that a critical landing page has been accidentally set to “noindex,” but an audit will catch it immediately.
Four Pillars of an SEO Audit
To make the auditing process manageable, we categorize checks into four distinct pillars. Each plays a vital role in your overall SEO performance.
1. On-Page SEO Signals
On-page SEO refers to the content and HTML source code of individual web pages.
This pillar ensures that search engines understand exactly what your content is about and which keywords you should rank for.
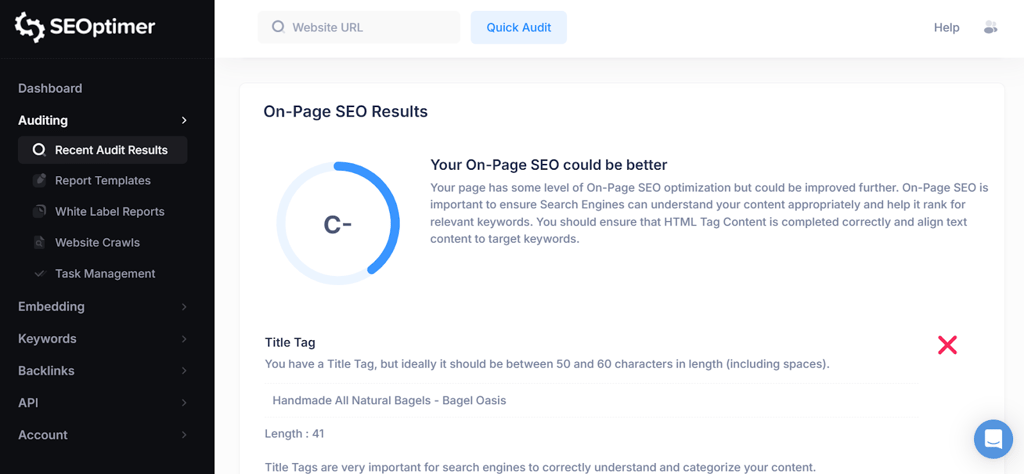
When you run an audit with SEOptimer, it checks critical on-page elements, including:
- Title Tags and Meta Descriptions: Are they unique, of the correct length, and optimized with target keywords?
- Header Tags (H1-H6): is your content structured logically? Search engines use headers to understand the hierarchy of your information.
- Keyword Consistency: Are you using your target keywords naturally throughout the content, image alt text, and headers?
- Content Volume: Do you have enough high-quality content on the page to satisfy user intent?
If your on-page signals are weak, search engines will struggle to connect your content with relevant search queries, no matter how great your writing is.
2. Technical SEO Foundations
Technical SEO is often the most intimidating pillar, but it is arguably the most important.
It involves the backend structure that allows search engines to crawl and index your site effectively.
If Google can’t crawl your site, you won’t rank. Period.
A robust audit looks for:
- Indexability: Are you accidentally blocking search engines with a misplaced “noindex” tag or a restrictive robots.txt file?
- XML Sitemaps: Do you have a valid sitemap submitted to search engines so they can find your pages?
- Canonical Tags: Are you properly handling duplicate content to ensure the right version of a page is indexed?
- SSL Security: Is your site secure (HTTPS)? Security is a confirmed ranking factor.
For a deeper dive, SEOptimer’s SEO Crawler scans every page of your site to uncover hidden technical issues that a standard surface-level check might miss.
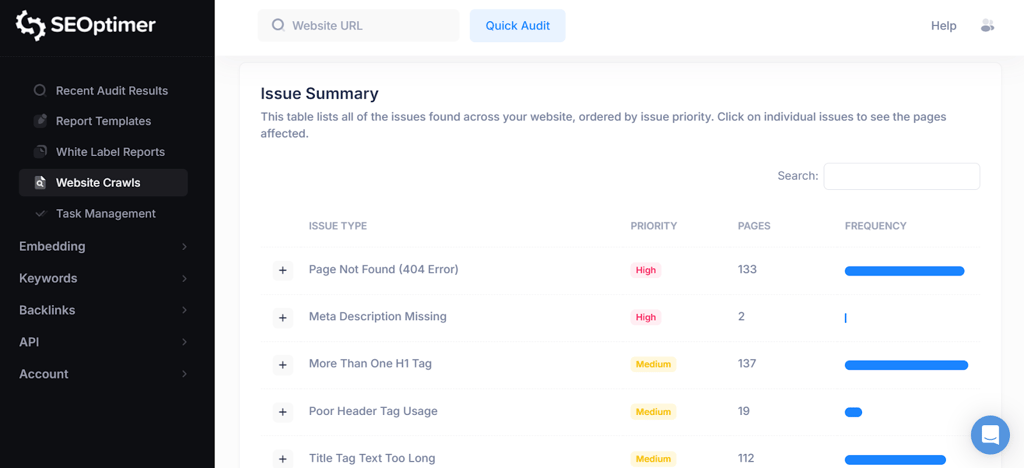
It uses advanced JavaScript rendering to load your site exactly like a real user (and modern search bots) would, ensuring no dynamic content or broken scripts go unnoticed.
3. Backlink Profile
Your backlink profile is a measure of your website’s authority and trustworthiness.
When other reputable sites link to you, it acts as a “vote of confidence” in the eyes of search engines.
An audit should analyze:
- Quantity and Quality: How many websites link to you, and do they have high domain authority?
- Toxic Links: Are there spammy or low-quality links pointing to your site that could trigger a penalty?
- Anchor Text: Is the text used in links relevant to your content?
For this, SEOptimer offers specialized Backlink Research and Backlink Monitoring tools.
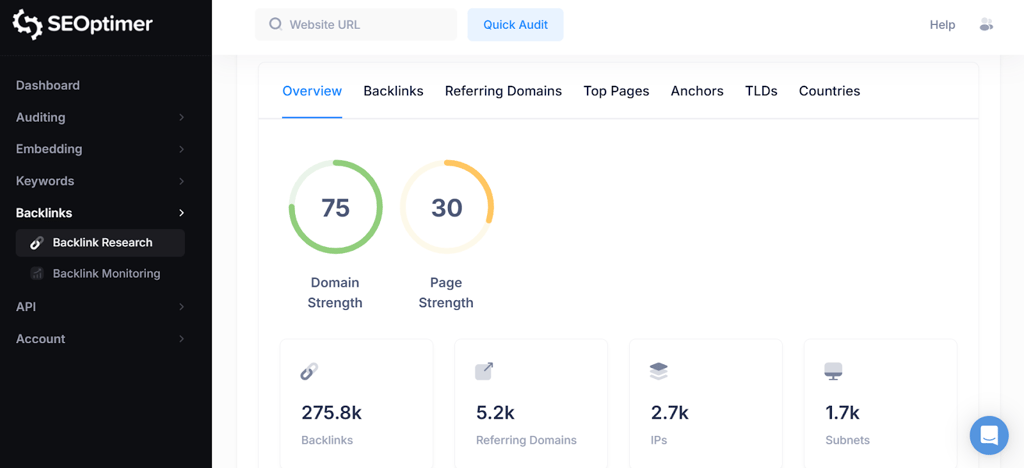
These features allow you to track new and lost links over time, view your top referring domains, and identify opportunities to build more authority in your niche.
4. Usability
Search engines prioritize the user. If your site is frustrating to use, your rankings will suffer. The Usability pillar focuses on the experience of the person behind the screen.
Key usability checks include:
- Mobile Responsiveness: With mobile-first indexing, your mobile site is now the primary version search engines use for ranking. Your audit must verify that viewports are set correctly and content renders perfectly on smartphones and tablets.
- Core Web Vitals: These are specific metrics related to speed, responsiveness, and visual stability.
- Page Speed: How fast does your content load? Slow sites lead to high bounce rates.
- Safe Browsing: Ensuring your site is free from malware and intrusive interstitials.
SEOptimer provides immediate feedback on these usability metrics, helping you identify if large images or unoptimized code are slowing down your user experience.
How Regular Should You Run SEO Audits?
SEO is not a one-time task; it is an ongoing process.
For most businesses, monthly audits are the standard recommendation.
A monthly cadence allows you to catch issues before they significantly impact your revenue, while giving you enough time to implement fixes between reports.
However, if you manage a large ecommerce site or publish content daily, you may need to audit weekly.
Fortunately, you don’t have to do this manually.
Most SEO auditing tools allow you to set up automated reporting.
Looks for tools that can schedule PDF reports to be generated and emailed to you (or your clients) daily, weekly, or monthly. This ensures you never miss a critical drop in health score or a new technical error.
Conclusion
Ignoring your website’s technical health is a risk you can’t afford to take.
By focusing on these four pillars, On-Page, Technical, Backlinks, and Usability, you build a website that is not only friendly to search engines but also enjoyable for your visitors.
Don’t wait for your traffic to drop before you take action.
Use a comprehensive SEO audit tool to see exactly where you stand. It’s the fastest way to turn hidden errors into ranking opportunities.












